We hope this article helped you understand how N/P is created and how interest affects the amount you pay the lender. One problem with issuing notes payable is that it gives the company more debt than they can handle, and this typically leads to bankruptcy. Issuing too many notes payable will also harm the organization’s credit rating. Another problem with issuing a note payable is it increases the organization’s fixed expenses, and this leads to increased difficulty of planning for future expenditures. For example, notes may be issued to purchase equipment or other assets or to borrow money from the bank for working capital purposes. It is important to realize that the discount on a note payable account is a balance sheet contra liability account, as it is netted off against the note payable account to show the net liability.
Notes Payable Issued to Bank
At the initial recognition, the notes are recorded at the face value minus any premium or discount or simply at its selling price. At subsequently, the accrued interest expense shall be carried before the installment is made to the lenders. Here, notes payable is a debit entry as it leaves no further liability. The cash account, however, has a credit entry, given the cash outflow in making repayments, which records a decreased asset. At the period-end, the company needs to recognize all accrued expenses that have incurred but not have been paid for yet.
Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
- Thus, S. F. Giant receives only $5,000 instead of $5,200, the face value of the note.
- In the preceding note, Oliva has agreed to pay to BancZone $10,000 plus interest of $400 on June 30, 20X8.
- This is because such an entry would overstate the acquisition cost of the equipment and subsequent depreciation charges and understate subsequent interest expense.
- In this journal entry, interest expenses is a debit entry, and interest payable is a credit entry, as a portion of it is yet to be paid.
- The impact of promissory notes or notes payable appears in the company’s financial statements.
This gives the company more time to make good on outstanding debt and gives the supplier an incentive for delaying payment. Also, the creation of the note payable creates a stronger legal position for the owner of the note, since the note is a negotiable legal instrument that can be more easily enforced in court actions. A short-term note payable is a debt created and due within a company’s operating period (less than a year). A short-term note is classified as a current liability because it is wholly honored within a company’s operating period.
Short-Term Note Payable – Discounted
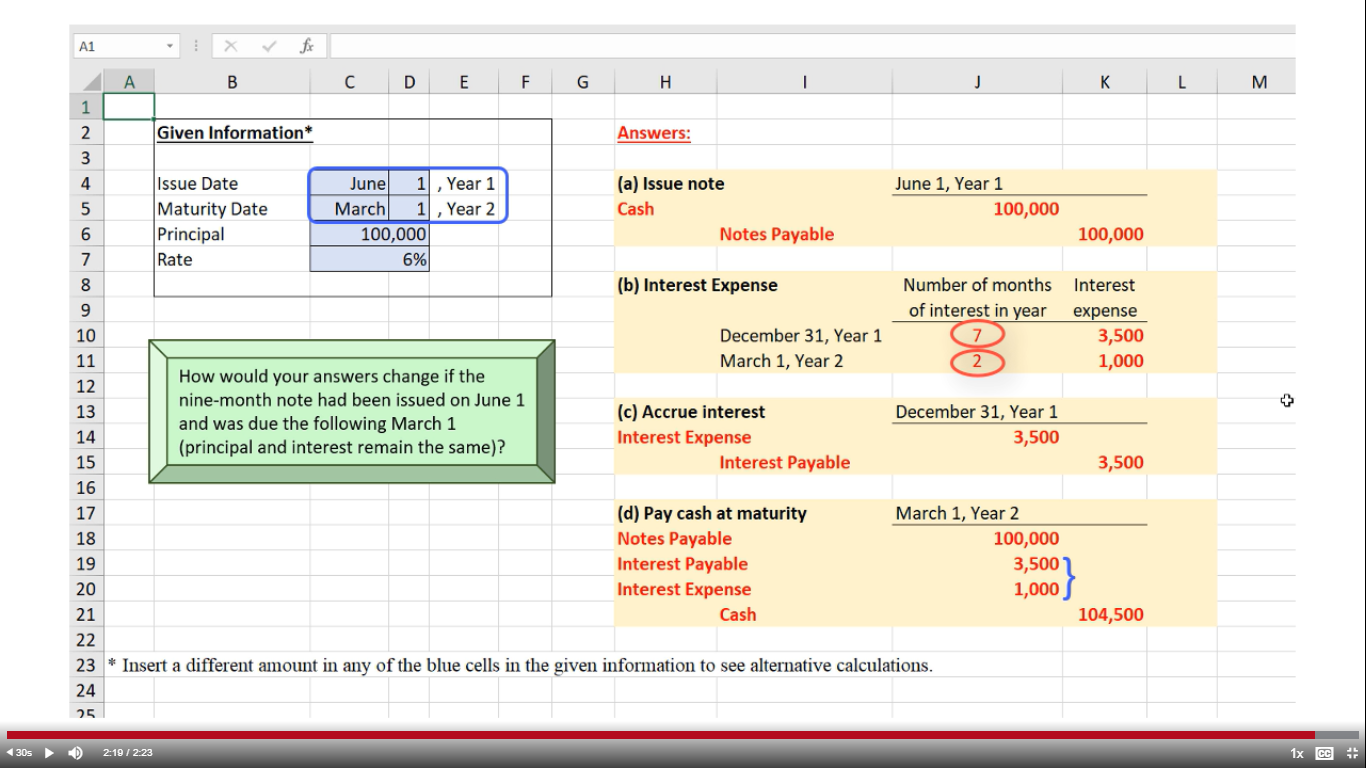
We also go over the components of journal entries and why they are important. Short-Term Notes Payable decreases (a debit) for the principalamount of the loan ($150,000). Interest Expense increases (a debit)for $4,500 (calculated as $150,000 principal × 12% annual interestrate × [3/12 months]). If you have ever taken out a payday loan, you may haveexperienced a situation where your living expenses temporarilyexceeded your assets.
Revenue and Expense Accounts
An amortization schedule shows you the monthly payments, interest charged, principal amortization, and outstanding balance. Discount amortization transfers the discount to interest expense over the life of the loan. This means that the $1,000 discount should be recorded as interest expense by debiting Interest Expense and crediting Discount on Note Payable. In this way, the $10,000 paid at maturity (credit to Cash) will be entirely offset with a $10,000 reduction in the Note Payable account (debit). A discount on a note payable is the difference between the face value and the discounted value at issuance. This interest expense is allocated over time, which allows for an increased gain from notes that are issued to creditors.
Journal Entry to Record Equipment Purchased and Issuance of Notes Payable
We encourage you to stay on top of your payables so that it won’t affect your creditworthiness. Some lenders dislike late payments, so if you always pay late, they may no longer grant you credit. Your credit score may also be affected if you always pay late, making it harder for you to secure loans or mortgages in the future. In the books of Evergreen Company, it must debit cash to signify the receipt of the note proceeds and credit note payables to signify its indebtedness.
At the origin of the note, the Discount on Notes Payable account represents interest charges related to future accounting periods. The interest portion is 12% of the note’s carrying value at the beginning of each year. The journal entry is also required when the discount is charged as an expense. We take monthly bookkeeping how to report farm rents on a schedule e off your plate and deliver you your financial statements by the 15th or 20th of each month. Accounts Payable decreases (debit) and Short-Term Notes Payableincreases (credit) for the original amount owed of $12,000. WhenSierra pays cash for the full amount due, including interest, onOctober 31, the following entry occurs.
The cash flow is discounted to a lesser sum that eliminates the interest component—hence the term discounted cash flows. The future amount can be a single payment at the date of maturity, a series of payments over future time periods, or a combination of both. A short-term notes payable created by a purchase typically occurs when a payment to a supplier does not occur within the established time frame. The supplier might require a new agreement that converts the overdue accounts payable into a short-term note payable (see Figure 12.13), with interest added.

Therefore, it must record the following adjusting entry on December 31, 2018 to recognize interest expense for 2 months (i.e., for November and December, 2018). National Company must record the following journal entry at the time of obtaining loan and issuing note on November 1, 2018. The notes payable is legally binding and signed by both parties, which need to stick to the points mentioned. It differs from Accounts Payable, which is used when firms purchase goods and services from the other party on credit and expect to pay for them later. The company ABC receives the money on the signing date and as agreed in the note, it is required to back both principal and interest at the end of the note maturity.
Weekly is good for moderate transaction volumes, and monthly works for most businesses with low transaction volumes. Reversing a journal entry is most common for entries for for recurring expenses or revenues. They can be reversed to avoid re-entering the same information each period. You can also do this for entries based on estimates, so you can adjust for actual amounts at the end of the period. Cash basis accounting is easier to implement and understand for small businesses with limited transactions and for personal finances. Accrual basis accounting is good for businesses with significant credit sales or deferred revenue.
So bezahlen diese Deutschen beim Onlineshopping
Online black colored jack specialist series large restrict position Slots!
Bet365 Casino Black-jack Experience What you need to Understand
Категорії новин
Категорії товарів
News categories
Product Categories
(095) 222 04 06 - служба доставки 1100 – 2200
Замовлення приймається до 2:30